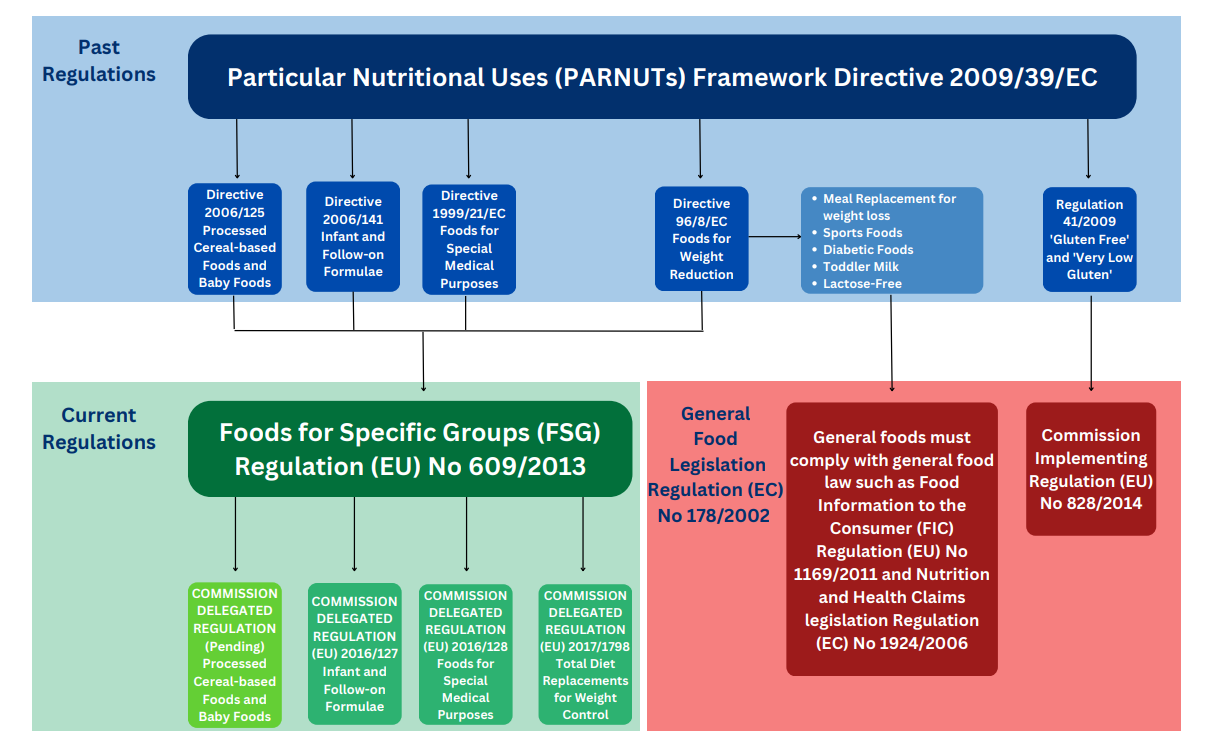
Regulation (EU) No 609/2013 repealed and replaced Directive 2009/39/EC on foodstuffs intended for particular nutritional uses (PARNUTS). The FSGs Regulation abolishes the concept of dietetic foods and provides for a new framework establishing general provisions for the limited number of well-established and defined categories of food that are considered as essential for certain vulnerable groups of the population.
Food Legislation Changes - Key Dates
| Date of Application | Action |
|---|---|
| 20 July 2016 |
Regulation (EU) No 609/2013 (Foods for Specific Groups) repeals Directive 2009/39/EC and allows for stocks, placed on the market or labelled before 20 July 2016 and which comply with Directive 2009/39/EC to remain on the market until these stocks are exhausted. Foods not covered by the new Foods for Specific Groups Regulation will fall under other general food law e.g. health claims, Food Information to the Consumer (FIC) |
| 22 Feb 2019 |
Dietary Foods for Special Medical Purposes Directive 1999/21/EC (Dietary Foods for Special Medical Purposes) is replaced by Regulation (EU) 2016/128 |
| 22 Feb 2020 | There is a longer transitional period for Food for Special Medical Purposes developed to satisfy the nutritional requirements of infants |
| 22 Feb 2020 |
Infant formulae and follow-on formulae Directive 2006/141/EC (Infant formulae and follow-on formulae) is replaced by Regulation (EU) 2016/127 |
| 22 Feb 2021 |
There is a longer transitional period for infant formula and follow-on formula manufactured from protein hydrolysates |
| 27 Oct 2022 |
Total diet replacement for weight control 27 Oct 2022 Directive 96/8/EC (Foods intended for use in energy-restricted diets for weight reduction) is replaced by Regulation (EU) 2017/1798 |
| No date as yet | Processed cereal-based foods and baby foods for infants and young children Current legislation (2006/125/EC) remains in force and more substantial work is being undertaken to form draft legislation |
FSG-REGULATION-(EU)-No-6092013.pdf
‘Gluten-free’ and very low gluten foods
‘Gluten free’ and ‘very-low gluten’ foods (Regulation EC 41/2009) that are pre-packed or loose are, since July 20th of 2016 governed by Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) No 828/2014.
An EU Commission report to the European Parliament and to the Council of 26 June 2008 on foods for persons suffering from carbohydrate metabolism disorders (diabetes) concluded that the scientific basis for setting specific compositional requirements is lacking. Specific rules have not been established in the FSGs Regulation for diabetic foods. Relevant claims will be considered for authorisation under Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006 on nutrition and health claims.
Report on food intended for sportspeople
Article 13 of Regulation (EU) No 609/2013 placed an obligation on the European Commission to produce, by 20 July 2015, a report on the necessity, if any, on provisions for food intended for sportspeople.
The report on food intended for sportspeople was adopted by the Commission to the European Parliament and The Council on 15 June 2016. This report from the Commission outlines that there will be no set rules for Sports foods. The Commission report is mainly based on the results of an external study commissioned by DG SANTE by the Food Chain Evaluation Consortium (FCEC) titled "Study on food intended for Sportspeople".
Report on Milk-based drinks and similar products intended for young children
Under the PARNUTS legislation growing up milks were considered a general PARNUT. Given the revisions under the FSGs Regulation milk-based drinks and similar products will no longer be regulated as a dietetic food.
Since 20 July 2016, young-child formulae placed on the market as “dietetic foods” has been classified as normal foods, fortified in certain nutrients, and targeting a specific sub-group of the population (i.e., young children).
Article 12 of Regulation (EU) No 609/2013 placed an obligation on the EU Commission to present to the European Parliament and to the Council, a report on the necessity, if any, of special provisions for milk-based drinks and similar products intended for young children.
This report on young-child formulae was adopted by the Commission on 31 March 2016 and was accompanied by an EU Staff Working Document.
What was PARNUTS?
Directive 2009/39/EC was referred foodstuffs intended for particular nutritional uses (PARNUTS) before the 20th of July 2016, when it was repealed and replaced by Regulation EU No 609/2013. PARNUTS where defined as “foodstuffs which, owing to their special composition or manufacturing process, are clearly distinguishable from foodstuffs for normal consumption, which are suitable for their claimed nutritional purposes, and which are marketed in such a way as to indicate such suitability”.